Software Architecture
The Illuminator consists of modular Python applications to perform simulations of energy systems. This section provides an overview of its software architecture. The diagram below describes the components of the Illuminator using the terminology of the C4 model.
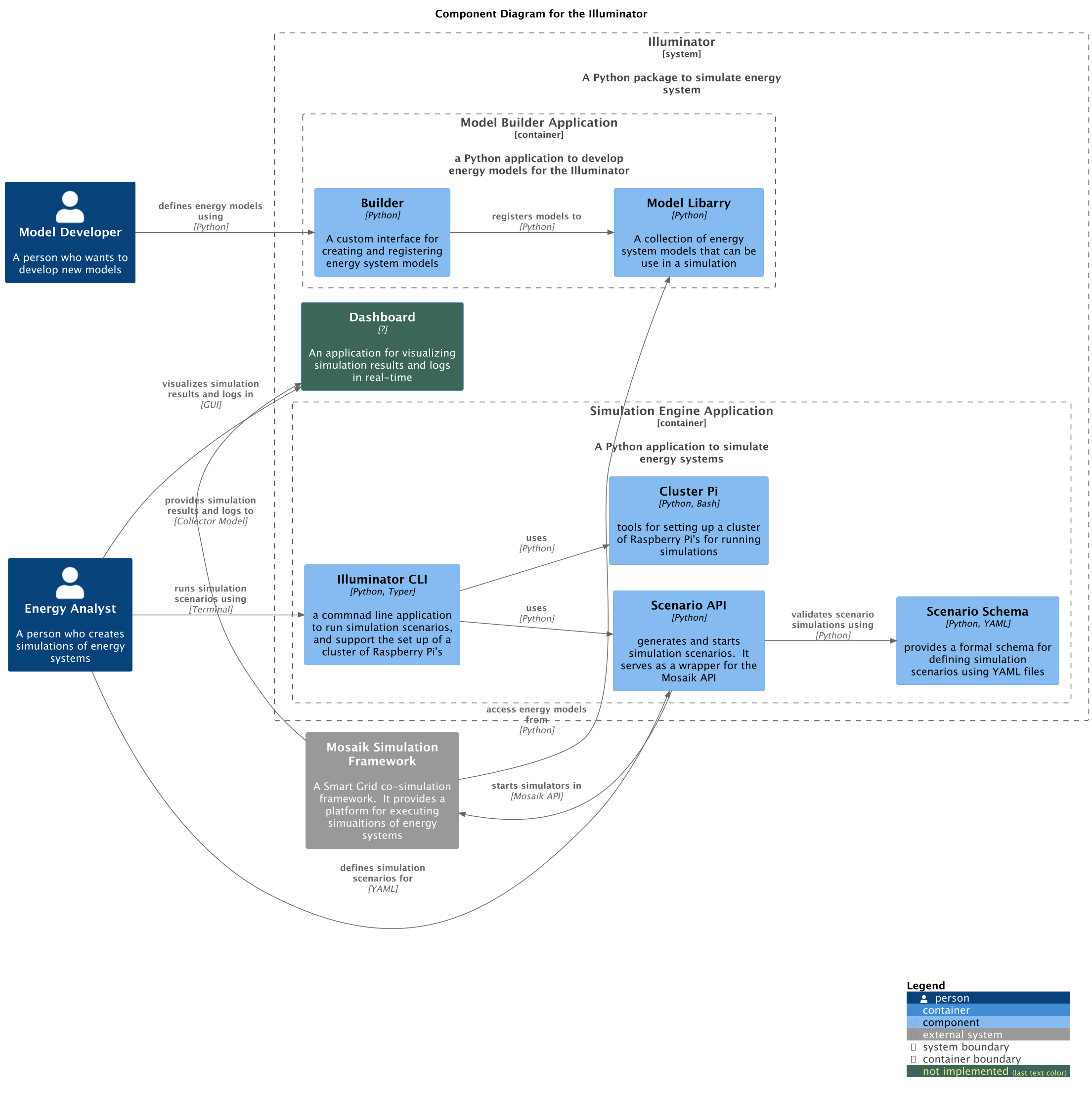
At a highest level, the Illuminator consists of three internal applications: Model Builder, Simulation Engie, and Dashboard; which depend on an an external application for executing simualation, the Mosaik Simulation Framework Users of the Illuminator interact with the Model Builder and the Simulation Engine for developig models and defining simulation scenarios. Illuminator’s applications interact with the Mosaik Simulation Framework to run simulations and collect the results.
Users
Users of the Illuminator take one of two roles:
Model Developer: uses the Illuminator to develops energy models that are registered into the application and can be used in a simulation by other users.
Energy Analyst: use the Illuminator to define and run simulations.
Components
Mosaik Simulation Framework
A framework that serves as the core platform for executing energy system simulations. Mosaik is an external dependency, and as such the Illuminator interacts with it through its API.
Model Builder Application
A Python application that model developers use to create/update energy models for the Illuminator. New models are developed using the Builder component, which provides a interface for creating and registering energy models to the Model Library. The purpose of the Builder component is to ease the development of energy models using a jargon that energy system engineers are more familiar with. For example, using term such as inputs, outputs, states, etc. to define new models.
The Model Library component stores energy models that can be use in a simulation, so that they can be accessed by the Mosaik Simulation Framework during runtime. Models in the Model Library are containers of metadata and business logic.
No computations related to simulations are performed by the model builder application.
Simulation Engine Application
A Python application to run simulations via the Mosaik API. This application consists of four components. The Scenario API provides a wrapper to prepare and start simulations in the Mosaik Simulation Framework. Simulations, computations and the management of output data are delegated to the Mosaik Simulation Framework. The Senario API uses the Scenario Schema to validate simulation scenarios writen as YAML files by the Energy Analysis. The Scenario Schema defines the format that YAML files must be written on.
The Illuminator CLI is an appliccation implemented using Typer, which provides a command line interface to run simulation locally, and parcially automates the deployment of the Illuminator in a Raspberry Pi cluster. The Illuminator CLI uses the Scernario API and the Cluster PI components to provide functionality.
Finally, the Cluster Pi component consists of a set of tools for setting up the Illuminator in a Raspberry Pi Cluster, where simulation scenarios can be run in a distributed mannern (e.i., each cluster node performs part of a simulation).
Dashboard
An application used by the Energy Analyst to visualise results and logs of simulations in real-time. This is has not been implemented in the current version.
Use Cases
There are three comon use cases for the users of the Illuminator:
Extending the model library: a Model developer wants to add a new model to the Model Library
Creating a simulation scenario: an Energy Analyst wants to define a simulation scenario using a YAML file and execute the simulation.
Set up a raspberry Pi Cluster: a user wants to set up the Illuminator in a cluster of Raspberry Pi’s to run simulations.
1. Extending the Model Library
Energy models should be added to the Model Library as follows:
Create a Python module with the name of the model. For example,
example_model.pyIn the file, create an IlluminatorModel object for the model. This defines which inputs, output, parameters, states, triggers, etc. a particular model has. For example:
from illuminator.builder import IlluminatorModel
# Defines a model'a paramters, inputs, outputs...
example_model = IlluminatorModel(
parameters={"param1": "addition"},
inputs={"in1": 10, "in2": 20},
outputs={"out1": 0},
states={"out1": 0},
time_step_size=1,
time=None
)
Create a class that inherits from
ModelConstructor, and impement thestep()method. The new class will become a model type in the Illuminator. Instances of this model type will be created by the Scenario API
For example,
from illuminator builder import ModelConstructor
class ExampleModel (ModelConstructor):
def step():
"""Computes this in every time step"""
# The computation logic goes here:
# return the time for the next time step
return time + self._model.time_step_size
Update the
illuminator/models/__init__.pyto import the new model type. For example:
from .example_model import ExampleModel
__all__ = ['BatteryModel',
'Collector',
'ExampleModel' # add new model
To test the new model has been added correctly, try to import it in a Python script:
# Python file
frmo illuminator.models import ExampleModel # test model import
# run the file to check if importing is successful
2. Creating Simulation Scenarios
Refer to simulation configuration file.
3. Setting Up Cluster Pi
Refer to Cluster Pi setup.